Traceability
Log AI decisions to allow traceable, auditable outcomes
“Traceability” ensures agent behavior is accountable and reviewable—over time, across sessions, and through multiple hands.
This principle supports transparency, troubleshooting, learning, and performance tuning. It is especially important in systems with high stakes or long histories.
Traceable agents
Log all actions taken, with timestamps and rationales.
Let users inspect differences between states.
Accept and incorporate user feedback on decisions.
Adjust future behavior based on interaction history.
Example Patterns
Session History
Scrollable timeline of actions with filters.
Change Diffing
Show what was added, removed, or modified.
Feedback Hooks
Allow users to mark decisions as good/bad.
Behavior Tuning
Refine future agent behavior based on user feedback or corrections.
Ideal for analytical tools, support dashboards, audit systems, or any environment where provenance, improvement, or rollback matters.
Action History
A chronological record of agent behavior supports traceability and builds long-term accountability in agentic systems.

What It Means
Keep a log of what the agent did, with when, why, and outcomes.
Why It Matters
Enables debugging, accountability, and learning.
When to Use This Principle
For complex systems with many agent actions, especially in compliance, legal, or regulated fields.
What it Looks Like in Action
A collapsible sidebar shows each action: “Summarized notes (1:02 PM) → Flagged inconsistencies → Suggested new section.”
Visual Diffing
Visual comparisons make agent-driven changes easier to audit and validate. This helps detect subtle alterations or unintended consequences.

What It Means
Graphically show what changed between agent and human versions.
Why It Matters
Supports clarity and reversibility.
When to Use This Principle
In content editing, code reviews, or document updates.
What it Looks Like in Action
Color-coded diffs like GitHub or “Track Changes,” highlighting additions/removals with hover explanations.
Feedback Hooks
Inviting user feedback creates a two-way relationship. It supports learning and allows agents to evolve based on real-world performance.

What It Means
Give users a way to respond to what the agent did.
Why It Matters
Enables learning loops and fine-tuning over time.
When to Use This Principle
After content generation, predictions, or decisions.
What it Looks Like in Action
After a chatbot answers a question, “Was this helpful?” appears with thumbs up/down. Selecting “No” opens a refinement prompt.
Behavior Tuning Over Time
Adaptive agents learn from usage and tune their actions to better suit user preferences. This supports trust, efficiency, and personalization.
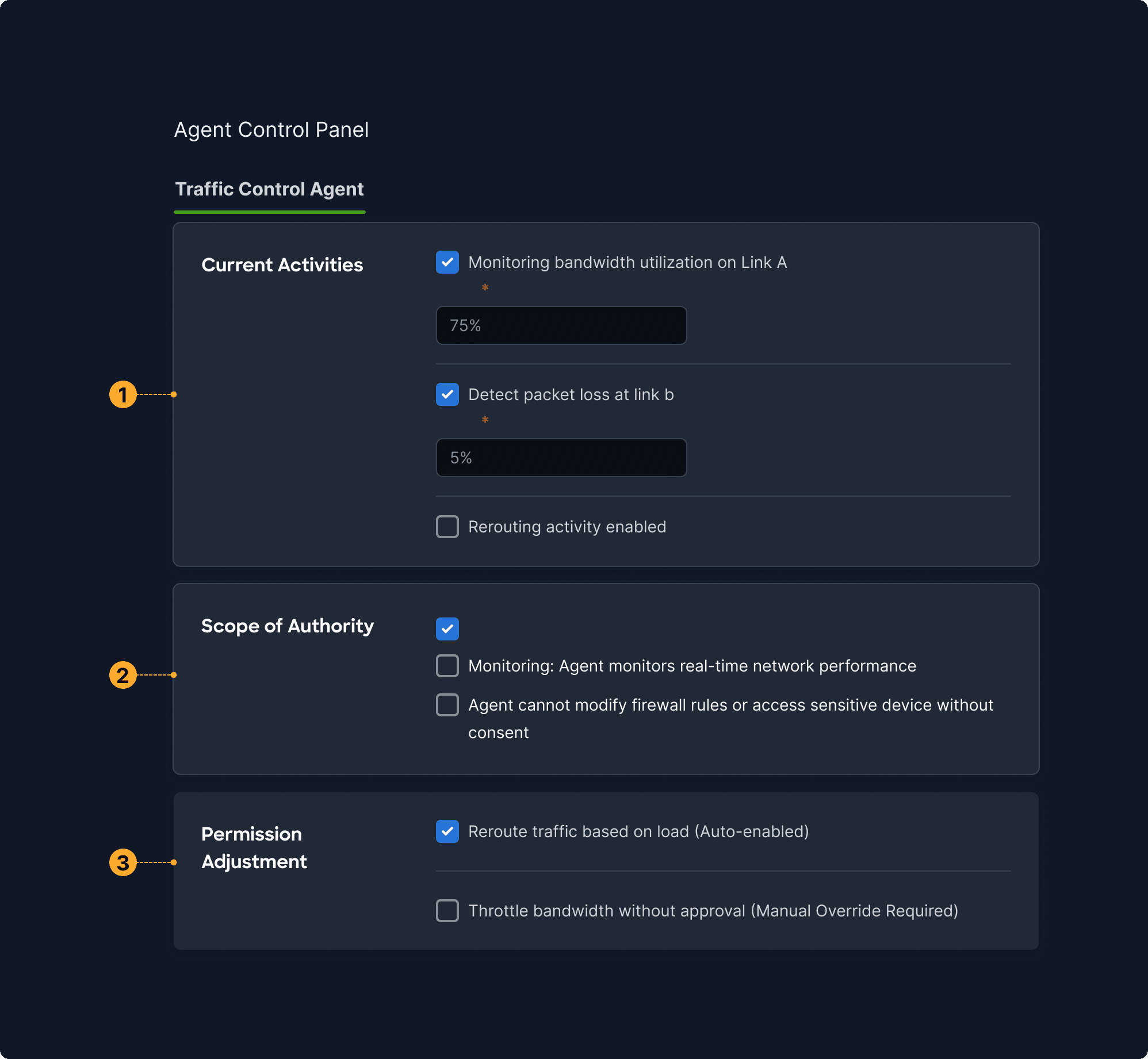
What It Means
Use interaction history and feedback to personalize future agent behavior.
Why It Matters
Increases usefulness and satisfaction while reinforcing long-term trust.
When to Use This Principle
In systems with repeat users or agent assistants operating over time.
What it Looks Like in Action
A “Behavior Settings” dashboard shows sliders for “Formality,” “Detail Level,” and remembers past overrides like “Stop suggesting meetings at 8 AM.”
Detailed Overview
Action History
Visual Diffing
Feedback hooks
Behavior Tuning Over Time