Clarity
Ensure the system is always explainable and visible

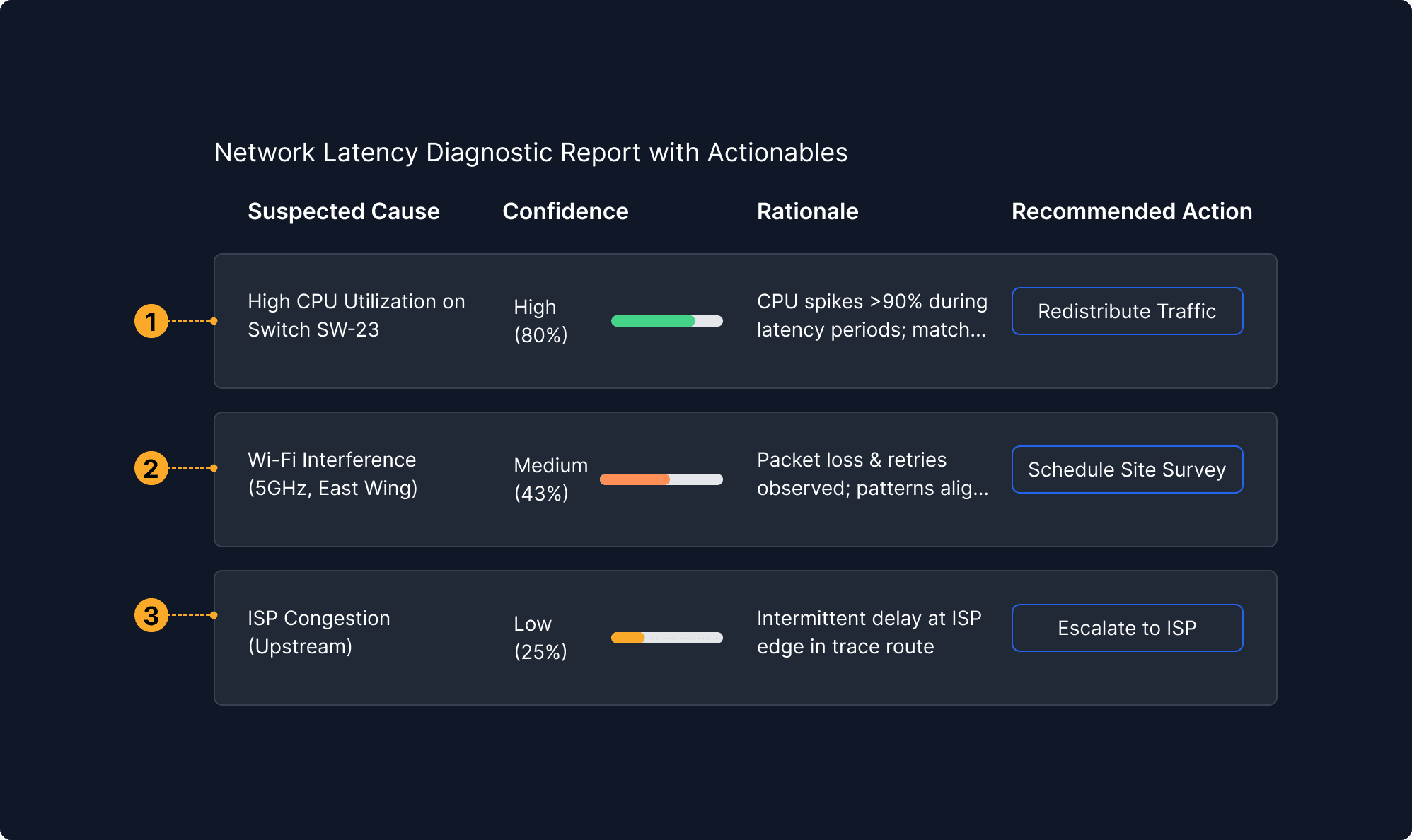
Suggested Action Cards
Lets users choose the intelligence level and cost, putting control over the AI’s “power” directly in their hands.
Tags
Fine-tunes the agent's behavioral flexibility—from creative to precise—giving nuanced control over outputs.
Action Context
Encourages exploration at the user's pace—only reveals complexity when the user is ready for it.
Status Indicators
Displays key network metrics (bandwidth, latency, packet loss) but does not provide confidence intervals or uncertainty information to support trust calibration.
Performance Trends
Shows historical and real-time trends of network metrics but lacks visual cues for data variability, measurement error, or forecast confidence.
Decision Logs
Records past actions and their outcomes but omits any expression of confidence or uncertainty about the effectiveness or reliability of those actions.
Decision Support
Offers recommended actions and simulations but fails to communicate the likelihood of success, risks, or uncertainty associated with those suggestions.
Custom Interaction
Enables user-defined commands without providing feedback on the confidence, risk, or expected impact variability of those custom actions.

Summary & Context
Provides a concise overview of the source of the problem, explaining what happened, where it happened, and what impact resulted. Helps users quickly verify the core source information behind the error.
Event & Time Tracking
Offers a detailed, timestamped sequence of source events leading to the error. Enables precise traceability and validation of when and how the problem originated and evolved.
Accountability & User Context
Identifies who is involved and which organization is responsible or reviewing, supporting accountability and giving provenance to the interaction with the data.

Summary & Context
Provides a concise overview of the source of the problem, explaining what happened, where it happened, and what impact resulted. Helps users quickly verify the core source information behind the error.
Event & Time Tracking
Offers a detailed, timestamped sequence of source events leading to the error. Enables precise traceability and validation of when and how the problem originated and evolved.
Accountability & User Context
Identifies who is involved and which organization is responsible or reviewing, supporting accountability and giving provenance to the interaction with the data.